Forget strategy, embrace agility
Mo Farah is an extraordinary athlete. During the course of his career, he has won double gold medals in the 5K and 10K races at the European Championships, the World Championships, and the Olympic Games. When asked about his formula for success, he has a simple answer: “Training, you just have to put in the training”. In reality, of course, the success of an athlete like Mo Farah is due to a wide variety of factors, including natural ability, race strategy, preparation, and execution.
Organizations, too, must balance different priorities to compete; yet they face much more uncertainty than an athlete like Mo Farah. A race is a well-defined event. The location, starting time, distance, competitors, and design of the track are all known in advance. The ‘playing field’ of business, however, is becoming less clear.
Unclear playing field
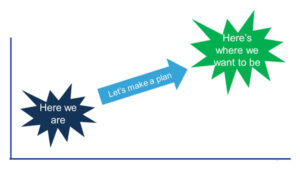
This lack of clarity is having a profound impact on the effectiveness of traditional strategies. Most strategy professors (myself included) describe strategy as a cascade of choices around where to play and how to win. Good strategy is based on using solid data and analysis to build an understanding of your current position, figure out a desired future position, and then design a plan to get from here to there (see Figure 1). I firmly believe that this model works. Or, at least it worked.
Figure 1: The Traditional View of Strategy
Today, I am no longer so sure…for a very simple reason: the business world is changing so quickly that predicting what the marketplace will look like in the future is becoming increasingly difficult. How many taxi companies incorporated the rise of Uber into their strategic planning processes? And why is it taking VW so long to react to its emissions crisis? In a constantly changing world, a long-term strategy can easily become an anchor that locks a company onto a path that is no longer relevant.
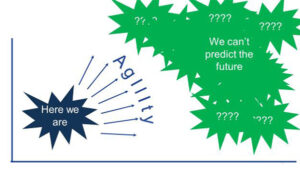
The key elements for success today are not plans and aspirations, but agility and capabilities. Capabilities (or access to capabilities) are required to compete effectively in a given position, and agility is required to make shifts in that position in response to a changing environment (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Emerging View of Strategy
Coming back to our athlete: Mo Farah succeeds not only because he is fast, but also because he adapts to the cadence of a race. He is a master of positioning, and he sets himself up for a winning finish. Sometimes he wins from the front, but more often than not, he comes from behind to take the lead in the final lap.
Farah has phenomenal capabilities but limited agility. He may be able to adapt to the changing dynamics of a race, but he would be completely lost if he had to compete in the high jump, on a bicycle, or on a tennis court. A more extreme form of agility is required by organizations as they move to the center of the digital vortex, an environment characterized by high market turbulence and shifting industry boundaries.
At the Global Center for Digital Business Transformation, an IMD and Cisco initiative, we define this extreme form of agility as digital business agility (DBA). DBA is composed of parts: hyperawareness, informed decision-making, and fast execution (see the article Disruptor and Disrupted: Strategy in the Digital Vortex for an in-depth explanation of these elements).
Staying aware of opportunities and threats
Hyperawareness is a company’s ability to detect and monitor changes in its business environment. Organizations need to be able to see opportunities and threats as they emerge. Most companies are only hyperaware about themselves! Often, they struggle to understand the changing dynamics within their industries. Much has been written about the dangers of organizational complacency, and this begins with a lack of hyperawareness.
However, hyperawareness is only valuable if the resulting data and information is used productively. Informed decision-making is a company’s ability to make the best decision possible in a given situation. To do this, data and information must be analyzed, scaled, packaged, and distributed throughout the organization. Data transparency, stable IT systems, advanced analytics, and a knowledge sharing culture play important roles in this capability.
Finally, informed decisions create value only to the extent that they can be implemented. Fast execution is a company’s ability to carry out its plans quickly and effectively. This is where the majority of organizations struggle the most. The capability to execute quickly requires a willingness to experiment and a tolerance for failure.
The traditional role of strategy is dead, but that does not mean that planning is also obsolete. A set of rolling short-term operational plans can be even worse than locking into a long-term objective. Plans are needed, but they must be constantly assessed and adapted along with changes in the environment. In some cases, they need to be discarded. Apple’s decision to enter the payments business, GE’s decision to divest GE Capital, and Tesla’s movement into battery production all represent significant shifts in direction based on a keen understanding of shifting marketplaces.
In the words of Manulife Financial CIO Joe Cooper, “Knowledge is a 20th century differentiator.” In the 21st Century, knowledge about the past is ubiquitous (Google knows it all), and the future is largely unknowable. Thus the ability to be agile – to sense, decide, and act quickly – will replace strategy as the key driver of organizational success in the future.
Michael Wade is the Cisco Chair in Digital Business Transformation, and Professor of Innovation and Strategic Information Management at IMD. His interests lie at the intersection of strategy, innovation, and digital transformation.
He is Director of the Global Center for Digital Business Transformation and co-Director of IMD’s new Leading Digital Business Transformation program (LDBT) designed for business leaders and senior managers from all business areas who wish to develop a strategic roadmap for digital business transformation in their organizations.
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
In the 2010s, card processing – Mastercard’s flagship service – started showing signs of commodification as new, nimble players (typically, fintech startups thriving on digital) entered the payment processing space, and customer preferences evolve...
The total costs of the Swiss healthcare system are rapidly approaching the CHF 100 billion mark per year. Now Switzerland is voting on November 24 on a further reform step. But that will not be enough. New ideas are needed.
COVID-19 challenges the value systems of family firms and urges them to adapt their behaviors, affecting their identities. This study aims to explore how and why family businesses strategically respond to challenges to their identity during COVID-...
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in NZZamSonntag 31 October 2024
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in I by IMD
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in Small Business Economics October 2024, vol. 63, pp. 993–1018, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-023-00846-3
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
IMD Center for Sustainable and Inclusive Business Report, October 2024
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications