
Structure and Drivers of Digital Competitiveness
Using the IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook’s data for 2016, we develop a measure of Digital Competitiveness; that is, the adequacy of the different components of an economy’s structure for facilitating its digitalization. We propose that in constructing such measure, there are three levels (i.e. factors) to be considered. These factors are:
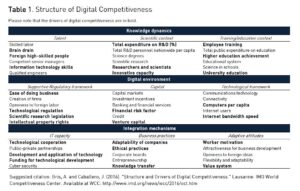
1) knowledge dynamics,
2) digital environment and
3) integration mechanisms.
Knowledge dynamics refer to the infrastructure necessary for the production of knowledge. For example, it takes into account the available talent, and the scientific and educational contexts.
The digital environment deals with the different frameworks that can facilitate the digitalization of an economy. These include the presence of a supportive regulatory framework, access to capital and the existence of an enabler technological framework. Knowledge production and the strength of the current digital environment would have a minimal impact without the presence of a set of mechanisms that allows for the absorption of new technologies.
We label the latter as integration mechanism which incorporate the IT capacity, business practices and the existence of adaptive attitudes. (We include the full structure of digital competitiveness in the link below).
The objective of this exercise is to identify the indicators that drive the digital competitiveness of a country. We do so by employing a statistical analysis which takes the digital competitiveness measure as the outcome and the different indicators as inputs. Due to space limitations we briefly discuss the results related to some key inputs but highlight all key drivers in the attached table. We found that in terms of talent the level of brain drain and access to foreign high-skilled people and to the information technology skills are statistically significant. In terms of the scientific context R&D expenditure, the availability of researchers and scientists and strong innovative capacity are fundamental. Among the important integration mechanisms it is worth highlighting, under business practices, the adaptability of companies, their ethical practices and the interactions (e.g., knowledge transfer) between the private sector and academia. In relation to adaptive attitudes, the motivation of the workforceand an “absorptive” value system are essential for digital competitiveness.
The highlighted results are indicative of the fundamental role of talent development and innovative capacity for attaining a fair digitalization level. In addition, the drivers of integration mechanisms underline the importance of developing a digitalization strategy that aligns multiple objectives such as the strategic adaptability to market changes, knowledge spillovers and a corporate culture driven by the production of knowledge and high levels of motivation among all levels of the corporate hierarchy.
It is important to point out that these results are preliminary and thus require further research. Our aim in introducing them has been to initiate a dialogue about the digital aspects of competitiveness.
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
- A new publication at the IMD World Competitiveness Center: The World Digital Competitiveness Ranking
- Structure and drivers of digital competitiveness
- A new publication at the IMD World Competitiveness Center: The World Digital Competitiveness Ranking
- Structure and drivers of digital competitiveness
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications

In the Building vs Buying Talent debate, internal growth reduces CEO risk—if leadership development and succession planning are aligned. Ric Roi shares how.

Regional developers have tried and failed to emulate Silicon Valley’s VC-driven model for innovation. Detroit Entrepreneurship is following an alternative route.

AI is reshaping careers, but future-proof skills aren’t what you think. Vision, expertise, and deep knowledge - not hype - are key to success in an AI world.

Tired teams, wasted weekends, and unread reports—here are 7 ways to restore morale and reignite performance. Avoid unnecessary reporting and non-essential tasks.

China's technology sector leads global innovation with AI, semiconductor growth, and strategic diversification. R&D investments fuel success amid regulatory challenges.

Explore eDNA science with Kristy Deiner on the IMD Management Cast . Learn how genetics, biodiversity, and data analytics shape conservation and the bioeconomy.
IMD produces a yearly Smart City Index offering a balanced focus on economic and technological aspects of smart cities on the one hand, and “humane dimensions” of smart cities (quality of life, environment, and inclusiveness) on the other. In this...

The case study introduces an original way of exploring the many questions and concerns around AI adoption in business. Based on a true story, it discusses the dilemma of AI implementation through Joe, the CIO of ParcelFlow. Joe is getting ready to...

How to avoid AI dystopia - We must fight against the convergence of micro-surveillance and digital inertia.

This case study explores AstraPay’s journey to become a significant player, despite its latecomer status, in Indonesia’s burgeoning digital payments landscape. Launched in 2018, AstraPay had grown to serve over one million customers, but it faced ...
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in I by IMD
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in I by IMD
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in I by IMD
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in I by IMD
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
IMD World Competitiveness Center Report, 8 April 2025
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Case reference: IMD-2650 ©2025
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications



